In a world where consumers wield power through their rights and product liability laws, a delicate dance unfolds between protection and responsibility. From the fundamental rights consumers hold dear to the intricate web of product safety standards, this topic delves into the heart of consumer advocacy and legal accountability.
Join us on a journey through the labyrinth of consumer protection agencies, legal recourse, and ethical considerations that shape our marketplace landscape.
As we navigate the complex terrain of consumer rights and product liability, we uncover the hidden truths and empowering knowledge that every consumer should possess.
Consumer Rights
Consumer rights refer to the fundamental entitlements that individuals have when purchasing goods or services. These rights are designed to protect consumers from unfair practices and ensure they are treated fairly in the marketplace.
Importance of Consumer Rights
Consumer rights play a crucial role in safeguarding individuals from exploitation and deception by businesses. By knowing their rights, consumers can make informed decisions, seek redress for faulty products or services, and hold companies accountable for any wrongdoing.
- Right to Safety: Consumers have the right to expect that the products they purchase are safe for use and do not pose any risks to their health.
- Right to Information: Consumers have the right to accurate and transparent information about the products or services they are buying, including pricing, ingredients, and potential risks.
- Right to Redress: Consumers have the right to seek compensation or replacement for defective products or unsatisfactory services.
- Right to Consumer Education: Consumers have the right to access resources and information to make informed choices and protect themselves in the marketplace.
Comparison of Consumer Rights Across Countries
Consumer rights can vary significantly from one country to another based on legal frameworks, cultural norms, and economic conditions. For example, some countries may have more robust consumer protection laws, while others may prioritize business interests over consumer rights.In the United States, consumer rights are primarily governed by federal laws such as the Consumer Product Safety Act and the Federal Trade Commission Act.
These laws aim to prevent fraud, deception, and unsafe products in the marketplace.On the other hand, European countries like the United Kingdom and Germany have strong consumer protection laws that cover a wide range of issues, including product safety, advertising standards, and unfair contract terms.Overall, while there may be differences in the specifics of consumer rights across countries, the underlying principle of protecting consumers from harm and ensuring fair treatment remains universal.
Product Liability Laws
Product liability refers to the legal responsibility of manufacturers, distributors, and sellers to ensure that their products are safe for consumer use. These laws are crucial in holding companies accountable for any harm caused by their products and are designed to protect consumers from defective or dangerous goods.
Types of Product Defects
- Design Defects: These occur when a product is inherently unsafe due to its design, even if manufactured correctly.
- Manufacturing Defects: These defects occur during the production process and can make a product dangerous or substandard.
- Marketing Defects: This includes inadequate instructions, warnings, or labeling that fail to inform consumers about potential risks associated with the product.
Variation Across Industries
Product liability laws can vary significantly across different industries, depending on the nature of the products involved and the potential risks they pose. Let’s explore how these laws differ in key sectors:
Automotive Industry
- Automotive manufacturers are subject to strict liability laws, holding them responsible for any defects in vehicles that cause harm to consumers.
- Recalls and safety standards are closely monitored in the automotive sector to ensure compliance with product liability regulations.
Pharmaceutical Industry
- Pharmaceutical companies face complex product liability challenges due to the potential health risks associated with drugs and medical devices.
- Strict regulations govern the testing, approval, and marketing of pharmaceutical products to protect consumers from harm.
Electronics Industry
- Electronic products, such as smartphones and laptops, are subject to product liability laws to ensure consumer safety and prevent malfunctions or hazards.
- Companies in the electronics industry must adhere to quality control measures and provide adequate warnings about potential risks associated with their products.
Consumer Protection Agencies
Consumer protection agencies play a crucial role in safeguarding the rights of consumers and ensuring fair practices in the marketplace. These agencies are tasked with enforcing consumer protection laws, investigating complaints, and educating the public about their rights.
Examples of Prominent Consumer Protection Agencies
- The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) in the United States is responsible for regulating financial products and services, enforcing consumer protection laws, and providing resources for consumers to make informed decisions.
- The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) oversees competition, consumer protection, and fair trading in Australia. It investigates complaints, enforces laws, and educates consumers and businesses about their rights and obligations.
- The European Consumer Centre (ECC) network provides assistance to consumers in the European Union, helping them resolve cross-border disputes and providing information on consumer rights within the EU.
Case Study: Successful Resolution by a Consumer Protection Agency
One notable case where a consumer protection agency successfully resolved a consumer complaint involved the ACCC in Australia. A consumer filed a complaint against a telecommunications company for misleading advertising and unfair contract terms. The ACCC investigated the matter, imposed fines on the company, and required them to change their advertising practices to comply with consumer protection laws.
This case highlights the important role consumer protection agencies play in holding businesses accountable and protecting consumers from deceptive practices.
Product Safety Standards

Product safety standards play a crucial role in ensuring the well-being of consumers and protecting manufacturers from liability issues. By adhering to these standards, companies can minimize the risk of producing faulty or dangerous products that could harm consumers.
The Process of Setting and Enforcing Product Safety Standards
Setting and enforcing product safety standards typically involves a collaborative effort between government regulatory agencies, industry stakeholders, and consumer advocacy groups. National standards are often established by government bodies such as the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) in the United States, while international standards may be developed by organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
- Government agencies conduct research and gather data to identify potential risks associated with certain products.
- Stakeholders participate in the development of standards through public consultations and meetings.
- Enforcement mechanisms, such as inspections and recalls, are implemented to ensure compliance with the established standards.
The Impact of Advancements in Technology on Evolving Product Safety Standards
Advancements in technology have led to the development of new products and materials, posing challenges for traditional safety standards. As products become more complex and interconnected, regulators must adapt and update standards to address emerging risks.
- Smart devices and IoT technologies require enhanced cybersecurity measures to protect consumer data and privacy.
- 3D printing and nanotechnology raise concerns about product quality and potential health hazards.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning introduce new considerations for product safety testing and risk assessment.
Consumer Complaint Resolution
In the realm of consumer rights and product liability, resolving complaints is a crucial aspect of ensuring customer satisfaction and maintaining trust in the marketplace. When consumers encounter issues with a product, whether it be a defect or dissatisfaction with its performance, knowing how to escalate complaints effectively can lead to a resolution that meets their needs.
Steps in Resolving Consumer Complaints
- 1. Contact the Company: Start by reaching out to the company directly through their customer service channels. Clearly explain the issue you are facing and provide any relevant details such as purchase information and product specifics.
- 2. Document Communication: Keep a record of all interactions with the company, including dates, times, and names of representatives spoken to. This documentation can be valuable if further action is needed.
- 3. Escalate the Issue: If initial contact does not lead to a satisfactory resolution, consider escalating the complaint to a higher level within the company. This may involve speaking with a supervisor or filing a formal complaint.
- 4. Seek External Assistance: If resolution is not achieved internally, consumers can turn to external resources such as consumer protection agencies or regulatory bodies. These organizations may provide guidance or intervene on behalf of the consumer.
- 5. Legal Action: As a last resort, consumers may consider legal action if their complaint remains unresolved. Consulting with a lawyer specializing in consumer rights can provide insight into potential legal options.
Tips for Effective Complaint Escalation
- 1. Be Clear and Concise: When communicating your complaint, provide specific details and avoid unnecessary information. Clear communication can help expedite the resolution process.
- 2. Stay Calm and Polite: While it can be frustrating to deal with product issues, maintaining a calm and polite demeanor can lead to more positive outcomes in resolving complaints.
- 3. Follow Up: Don’t be afraid to follow up on your complaint if you haven’t received a response within a reasonable timeframe. Persistence can demonstrate the seriousness of your concerns.
- 4. Know Your Rights: Familiarize yourself with consumer rights laws and protections in your jurisdiction. Understanding your rights can empower you in resolving complaints effectively.
- 5. Consider Alternative Solutions: In some cases, companies may offer alternative solutions such as replacements, refunds, or repairs. Be open to exploring these options to reach a resolution that satisfies both parties.
Real-Life Example of Consumer Complaint Resolution
A consumer purchased a faulty electronic device and encountered issues with its functionality shortly after the purchase. Despite initial attempts to resolve the complaint with the company’s customer service, the problem persisted. The consumer then sought assistance from a consumer protection agency, which mediated the dispute and facilitated a full refund for the defective product.
Legal Recourse for Consumers
Consumer protection laws provide a safety net for individuals who have suffered injuries or damages due to faulty products. In such cases, consumers have several legal options available to seek compensation and justice for their losses.
Class-Action Lawsuits
Class-action lawsuits play a crucial role in addressing widespread product defects or safety issues that affect a large group of consumers. By consolidating individual claims into a single lawsuit, class actions enable consumers to hold manufacturers and sellers accountable for their actions.
This collective legal action can also lead to more significant settlements and changes in industry practices to prevent future harm.
- Pros of Class-Action Lawsuits:
- Efficiency: Streamlines the legal process and reduces individual litigation costs.
- Strength in Numbers: Increases leverage against powerful corporations.
- Compensation: Provides a way for consumers to receive fair compensation for their losses.
- Cons of Class-Action Lawsuits:
- Complexity: Managing a large group of plaintiffs and different claims can be challenging.
- Settlement Amounts: Individual compensation may be lower than in individual lawsuits.
- Lengthy Process: Class actions can take years to resolve, delaying justice for some consumers.
Legal Action vs. Alternative Dispute Resolution
When faced with product-related injuries or damages, consumers must weigh the pros and cons of pursuing legal action versus seeking alternative dispute resolution methods, such as arbitration or mediation.
- Legal Action:
- Strength of Legal Rights: Provides a formal legal process to seek compensation and hold accountable those responsible for the harm.
- Potential for Higher Damages: Court judgments may result in larger compensation amounts compared to settlements in alternative dispute resolution.
- Public Awareness: Lawsuits can raise awareness about product safety issues and prompt recalls or changes in industry practices.
- Alternative Dispute Resolution:
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive and faster than going to court.
- Confidentiality: Offers a private and less adversarial way to resolve disputes.
- Limited Legal Recourse: Consumers may forfeit their right to pursue further legal action by agreeing to alternative dispute resolution methods.
Consumer Education Initiatives
Consumer education plays a crucial role in empowering individuals to make informed purchasing decisions. By providing consumers with the necessary knowledge and skills, they can better understand their rights, evaluate product safety, and avoid falling victim to deceptive practices in the market.Successful consumer education campaigns have shown a significant impact on consumer behavior.
For example, campaigns that focus on educating consumers about their rights regarding refunds and warranties have led to an increase in the number of people seeking redress for faulty products. Similarly, initiatives that raise awareness about product safety standards have resulted in a decrease in the number of injuries caused by unsafe products.Schools, universities, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a vital role in promoting consumer education.
Integrating consumer education into school curriculums helps young individuals develop critical thinking skills and understand the importance of being informed consumers. Universities can offer specialized courses on consumer rights and product liability laws to equip students with the knowledge needed to navigate the market effectively.
NGOs often organize workshops, seminars, and awareness campaigns to educate the public about their rights and responsibilities as consumers.
Role of Schools in Consumer Education
Schools serve as a primary platform for instilling consumer education in students from a young age. By integrating consumer rights and responsibilities into the curriculum, schools can help students develop a sense of awareness and empowerment when making purchasing decisions.
Through interactive activities and real-life case studies, students can learn about the importance of reading product labels, understanding warranties, and seeking redress for faulty products.
NGO Initiatives in Consumer Education
Non-governmental organizations play a crucial role in promoting consumer education through various initiatives. These organizations often collaborate with government agencies, consumer protection bodies, and educational institutions to raise awareness about consumer rights and product safety. By organizing workshops, seminars, and social media campaigns, NGOs can reach a wider audience and empower consumers to make informed choices.
Additionally, they provide resources and support to individuals facing consumer issues, guiding them on how to seek redress and protect their rights.
Ethical Considerations in Product Marketing
In the realm of product marketing, ethical considerations play a crucial role in safeguarding consumer rights and ensuring transparency in business practices. Companies must adhere to ethical standards to build trust with consumers and maintain their loyalty.
Deceptive Marketing Practices
Deceptive marketing practices can have detrimental effects on consumers, leading them to make uninformed decisions about the quality or safety of a product. This can include false advertising, misleading claims, or omitting crucial information that impacts consumer choices.
- Companies should refrain from making false claims about their products’ benefits or features to manipulate consumer perceptions.
- Transparency in marketing communication is essential to provide accurate information to consumers and prevent any misleading tactics.
- It is crucial for companies to ensure that their marketing campaigns are honest, truthful, and in compliance with consumer protection laws.
- Regular monitoring and review of marketing strategies can help identify and rectify any deceptive practices before they harm consumers.
International Trade and Consumer Rights
International trade agreements play a significant role in shaping consumer rights protection around the world. These agreements can impact the regulations that govern consumer protection, as well as the enforcement mechanisms in place to ensure those rights are upheld.
Impact of International Trade Agreements
International trade agreements can either strengthen or weaken consumer rights protection, depending on the specific provisions included. For example, trade agreements may include clauses that prioritize free trade over consumer protection, leading to potential conflicts between the two objectives.
Comparison of Consumer Rights Regulations
Developed countries often have more robust consumer rights regulations compared to developing nations. This disparity can create challenges for consumers in developing countries, where legal protections may be limited, and enforcement mechanisms may be weaker.
Enforcing Consumer Rights in a Global Marketplace
Enforcing consumer rights in a global marketplace with diverse regulatory frameworks poses a significant challenge. Different countries may have varying standards for product safety, labeling requirements, and dispute resolution mechanisms, making it difficult to ensure consistent protection for consumers worldwide.
Emerging Trends in Consumer Protection
Consumer protection efforts are constantly evolving to keep up with the changing landscape of technology and consumer behavior. In this digital age, new trends and technologies are shaping the way consumer rights are advocated for and protected. Social media and online reviews play a significant role in influencing consumer choices and holding businesses accountable for their products and services.
As we look towards the future, it is important to predict the developments in consumer protection laws and consider their implications for both businesses and consumers.
Role of Artificial Intelligence in Consumer Protection
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way consumer protection agencies monitor and enforce regulations. AI-powered tools can analyze large amounts of data to detect patterns of consumer harm, identify deceptive practices, and predict potential risks to consumers. By leveraging AI technology, regulatory bodies can proactively address consumer issues and protect the public from harm.
Impact of Blockchain Technology on Product Transparency
Blockchain technology is enhancing product traceability and transparency, allowing consumers to verify the authenticity and origin of products. Through blockchain-enabled supply chains, consumers can track the journey of a product from its creation to its sale, ensuring quality control and reducing the risk of counterfeit goods.
This increased transparency empowers consumers to make informed decisions and hold companies accountable for the products they deliver.
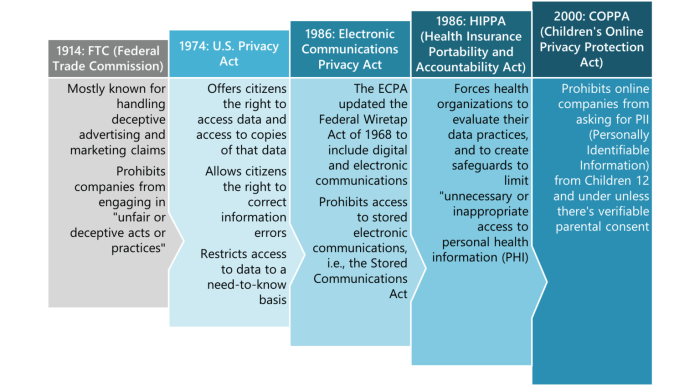
Rise of Consumer Data Privacy Regulations
With the growing concerns about data privacy and security, there is a rising trend in implementing stricter regulations to protect consumer information. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States are setting new standards for data protection and giving consumers more control over their personal information.
Businesses are now required to be more transparent about their data practices and obtain explicit consent from consumers before collecting their data.
Case Studies on Consumer Rights Violations
Consumer rights violations by businesses can have far-reaching consequences, impacting not only the affected consumers but also the reputation and bottom line of the companies involved. Let’s delve into some notable case studies to understand the repercussions and lessons learned from these incidents.
Volkswagen Emissions Scandal
The Volkswagen emissions scandal, also known as “Dieselgate,” is a prime example of a major consumer rights violation. In 2015, it was revealed that Volkswagen had installed software in their diesel vehicles to cheat emissions tests. This deceitful practice led to higher levels of harmful pollutants being emitted into the environment than what was reported.
As a result, Volkswagen faced hefty fines, recalls of millions of vehicles, and a significant blow to their reputation. This case highlighted the importance of transparency, honesty, and adherence to environmental regulations in the automotive industry.
Wells Fargo Unauthorized Accounts Scandal
Another infamous case of consumer rights violations is the Wells Fargo unauthorized accounts scandal. In 2016, it was uncovered that employees at Wells Fargo had opened millions of unauthorized accounts in customers’ names without their consent. This unethical behavior was driven by aggressive sales targets and incentives within the bank.
Wells Fargo faced a wave of lawsuits, regulatory investigations, and a tarnished reputation. This case underscored the need for strict oversight of sales practices and the prioritization of customer interests over corporate goals.
Facebook Cambridge Analytica Data Breach
The Facebook Cambridge Analytica data breach is a significant case that raised concerns about consumer data privacy and protection. In 2018, it was revealed that the political consulting firm Cambridge Analytica had harvested the personal data of millions of Facebook users without their consent for political advertising purposes.
This breach led to a massive backlash against Facebook, with allegations of inadequate data protection measures and violations of user privacy. The incident prompted increased scrutiny of data handling practices by tech companies and sparked discussions on the need for stronger data protection regulations.
Lessons Learned and Policy Impact
These case studies serve as cautionary tales for businesses, highlighting the importance of ethical conduct, transparency, and respect for consumer rights. The consequences faced by companies involved in consumer rights violations are severe, ranging from legal penalties and financial losses to reputational damage and loss of consumer trust.
As a result, policymakers have been spurred to enact stricter regulations, enhance consumer protection measures, and enforce penalties for non-compliance. These incidents have reshaped the landscape of consumer rights and influenced the development of policies that prioritize consumer welfare and hold businesses accountable for their actions.
Final Wrap-Up
As we conclude our exploration of consumer rights and product liability, the tapestry of regulations and ethical considerations comes into focus. From the echoes of past violations to the promise of emerging trends, the roadmap to a fair and just marketplace unfolds before us.
Let us carry forward this torch of consumer empowerment and protection, shaping a future where rights are upheld and products are safe.