Data Privacy Laws sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with humor with funny tone style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Ever wonder how laws protect your data in this digital age full of cat videos and memes? Well, get ready to dive into the wild world of Data Privacy Laws, where regulations are as complex as choosing the perfect filter for your selfie.
Overview of Data Privacy Laws
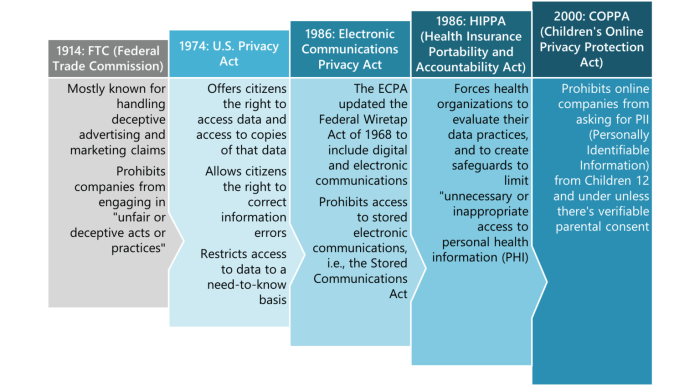
Data privacy laws have evolved over time in response to the increasing digitalization of our world. The need to protect personal information and data from misuse and unauthorized access has become paramount in today’s society.
Development of Data Privacy Laws
Data privacy laws can trace their origins back to the 1970s when countries like Sweden and Germany enacted the first laws to protect personal data. The landmark legislation, the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), was implemented in 2018, setting a global standard for data protection.
Objectives of Data Privacy Laws
- Safeguarding individuals’ personal information from unauthorized access and misuse.
- Ensuring transparency and accountability in the handling of personal data by organizations.
- Empowering individuals with control over their own data and privacy rights.
Significance of Data Privacy Laws in the Digital Age
In today’s digital age, where data is constantly being generated and shared online, data privacy laws play a crucial role in protecting individuals’ privacy rights. They help in building trust between consumers and businesses, fostering a secure online environment, and ensuring the responsible use of personal data.
Types of Data Privacy Laws
Data privacy laws vary in scope and impact, with different regulations tailored to specific industries and regions. Let’s compare and contrast some of the key data privacy laws, such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA, and explore their provisions and effects on businesses.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR is a comprehensive data privacy law that applies to businesses operating within the European Union (EU) or handling EU citizens’ personal data. Key provisions include:
- Requirement for explicit consent for data processing.
- Right to access and rectify personal data.
- Mandatory data breach notification within 72 hours.
Industries impacted by GDPR include technology companies, e-commerce platforms, and multinational corporations with operations in the EU.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA is a state-level data privacy law in California, providing consumers with more control over their personal information. Key provisions include:
- Right to know what personal data is collected and how it is used.
- Right to opt-out of the sale of personal information.
- Right to request deletion of personal data.
CCPA primarily affects companies with a presence in California or engaging with California residents, impacting sectors like retail, advertising, and technology.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
HIPAA is a federal law in the United States that safeguards protected health information (PHI) and sets standards for healthcare data privacy and security. Key provisions include:
- Requirements for healthcare providers to protect patient information.
- Limitations on the use and disclosure of PHI.
- Imposition of penalties for violations of patient privacy rights.
HIPAA primarily affects healthcare providers, insurance companies, and related entities handling sensitive medical data.
Compliance Requirements
Ensuring compliance with data privacy laws is crucial for organizations to protect sensitive information and maintain trust with their customers. Failure to comply can result in severe consequences, including fines and damage to reputation. Here, we will explore the common compliance requirements, consequences of non-compliance, and best practices for organizations to follow.
Common Compliance Requirements
- Implementing security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
- Obtaining explicit consent from individuals before collecting or processing their personal information.
- Providing individuals with access to their data and allowing them to request corrections or deletions.
- Regularly conducting privacy impact assessments to identify and mitigate risks to data privacy.
- Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee compliance with data privacy laws.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
- Hefty fines imposed by regulatory authorities for violations of data privacy laws.
- Lawsuits from affected individuals for damages resulting from data breaches or misuse of personal information.
- Reputational damage that can lead to loss of customer trust and business opportunities.
- Potential suspension of data processing activities until compliance is achieved.
Best Practices for Compliance
- Regularly review and update data privacy policies and procedures to align with current regulations.
- Provide comprehensive training to employees on data protection practices and the importance of compliance.
- Conduct regular audits and assessments to identify and address any gaps in data privacy measures.
- Establish clear procedures for responding to data breaches and notifying affected individuals as required by law.
- Monitor changes in data privacy laws and adjust compliance strategies accordingly to stay ahead of regulatory requirements.
Data Protection Measures
Data protection measures are crucial in ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive information. One of the key requirements mandated by data privacy laws is the implementation of robust measures to safeguard data from unauthorized access and misuse. Encryption plays a significant role in achieving this goal by encoding data in a way that only authorized parties can decipher it.
Additionally, data breaches have underscored the importance of stringent data protection measures, as they can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations alike.
Role of Encryption in Safeguarding Data Privacy
Encryption is a fundamental tool in protecting data privacy by converting plain text into ciphertext, making it unreadable to anyone without the decryption key. This ensures that even if unauthorized parties gain access to the data, they cannot decipher it without the proper authorization.
By encrypting sensitive information, organizations can mitigate the risk of data breaches and uphold the confidentiality of personal data.
- Encryption algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) are commonly used to secure data at rest and in transit.
- End-to-end encryption protocols ensure that data remains encrypted throughout its entire journey, from sender to recipient.
- Implementing encryption best practices, such as key management and regular updates to encryption protocols, is essential for maintaining data security.
Impact of Data Breaches on the Importance of Data Protection Measures
Data breaches have far-reaching consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal ramifications. These incidents highlight the critical need for robust data protection measures to prevent unauthorized access and mitigate the impact of security breaches.
Data breaches can result in the exposure of sensitive personal information, leading to identity theft, fraud, and other forms of cybercrime.
- Organizations that fail to implement adequate data protection measures may face regulatory fines and lawsuits for non-compliance with data privacy laws.
- Data breaches erode consumer trust and confidence, potentially leading to loss of customers and business opportunities.
- Investing in comprehensive data protection strategies, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, is essential for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining trust with stakeholders.
International Implications
When it comes to data privacy laws, navigating the international landscape can be quite challenging for businesses and organizations. Each country has its own set of regulations and compliance requirements, making it difficult to ensure consistency and uniformity across borders.
Challenges of Complying with Data Privacy Laws Across Different Countries
One of the main challenges of complying with data privacy laws across different countries is the varying legal frameworks and requirements. What may be considered acceptable data practices in one country could be a violation of privacy laws in another.
This makes it crucial for organizations to stay informed and updated on the specific regulations of each country they operate in or transfer data to.
Concept of Data Localization and Its Relevance
Data localization refers to the practice of storing and processing data within the borders of a specific country. This concept is relevant in the context of international data privacy laws as some countries require personal data of their citizens to be stored locally.
This can pose challenges for organizations that operate globally and need to transfer data across borders while complying with data localization requirements.
Examples of Cross-Border Data Transfer Regulations
- EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The GDPR imposes strict regulations on the transfer of personal data outside the European Economic Area (EEA). Organizations must ensure that data transfers to countries outside the EEA meet certain criteria for adequacy or implement appropriate safeguards.
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Privacy Framework: APEC member economies have established guidelines for cross-border data transfers, emphasizing the importance of accountability, security, and transparency in handling personal information.
- California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): The CCPA includes provisions for cross-border data transfers and requires businesses to disclose if they transfer personal data to third parties outside of the United States.
Consumer Rights
Consumer rights are an essential component of data privacy laws, ensuring that individuals have control over their personal information and how it is used by organizations. These rights grant consumers the power to make informed decisions about their data and hold companies accountable for any misuse or mishandling of their information.
Rights Granted to Consumers
- Right to access: Consumers have the right to access the personal data that companies hold about them and how it is being used.
- Right to rectification: Individuals can request corrections to any inaccurate or incomplete data held by organizations.
- Right to erasure: Also known as the “right to be forgotten,” this allows consumers to request the deletion of their personal data under certain circumstances.
- Right to data portability: Consumers can request their data in a commonly used format to transfer to another service provider.
- Right to object: Individuals can object to the processing of their data for marketing purposes or based on legitimate interests.
Mechanisms for Exercising Rights
- Online portals: Many companies provide online platforms where consumers can easily access, rectify, or delete their personal data.
- Data protection officers: Organizations are required to appoint data protection officers who can assist consumers in exercising their privacy rights.
- Complaint procedures: Consumers can file complaints with data protection authorities if they believe their rights have been violated.
Effectiveness of Consumer Protection Provisions
The effectiveness of consumer protection provisions in data privacy laws varies depending on enforcement mechanisms, penalties for non-compliance, and awareness among individuals.
Strong enforcement by regulatory bodies, hefty fines for violations, and proactive measures by organizations to comply with consumer rights can enhance the effectiveness of these provisions. However, challenges such as lack of awareness among consumers and resource constraints in regulatory agencies can hinder the full realization of consumer protection in data privacy laws.
Business Impact
Data privacy laws have a significant impact on businesses of all sizes, influencing their operations, finances, and reputation. Compliance with these laws is essential to maintain consumer trust and protect company data.
Impact on Businesses
Implementing compliance measures for data privacy laws can be costly for businesses, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with limited resources. The expenses associated with ensuring data protection, conducting audits, training employees, and implementing security measures can add up quickly.
Larger corporations may have more financial resources to allocate towards compliance, but the costs can still be substantial.
Consumer Trust and Brand Reputation
Data privacy laws play a crucial role in influencing consumer trust and brand reputation. Businesses that prioritize data protection and privacy are more likely to gain the trust of their customers, leading to enhanced brand loyalty and positive reputation. On the other hand, companies that fail to comply with data privacy laws risk losing consumer trust, which can have long-lasting detrimental effects on their brand reputation and bottom line.
Evolving Landscape
The landscape of data privacy laws is constantly evolving to keep up with advancements in technology and the changing ways in which data is collected, stored, and used. As new trends and developments emerge, regulations are adapted to address the challenges posed by these changes.
Recent Trends and Developments
In recent years, there has been a notable shift towards more stringent data privacy regulations around the world. Countries are enacting comprehensive laws, such as the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California, to enhance the protection of personal data.
These laws place greater emphasis on transparency, consent, and accountability in data processing activities.
- Increased Focus on Data Breach Notification: Many jurisdictions are implementing mandatory data breach notification requirements to ensure that individuals are promptly informed when their personal information is compromised.
- Rise of Data Localization Laws: Some countries are introducing data localization requirements, which mandate that certain types of data must be stored within the country’s borders. This trend aims to enhance data security and sovereignty.
- Emphasis on Data Protection Impact Assessments: Data protection impact assessments are becoming a standard practice for organizations to evaluate the potential risks associated with their data processing activities and implement appropriate safeguards.
Implications of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Internet of Things (IoT) present new challenges for data privacy regulations. These technologies often involve the processing of vast amounts of data, raising concerns about consent, transparency, and algorithmic bias. Regulators are working to update existing laws to address these challenges and ensure that individuals’ rights are protected.
- AI and Machine Learning: The use of AI algorithms for automated decision-making raises questions about how to ensure fairness and accountability in data processing. Regulators may introduce guidelines for ethical AI development to mitigate potential risks.
- IoT Security: The proliferation of IoT devices collecting sensitive data poses security risks and vulnerabilities. Data privacy laws may require manufacturers to implement robust security measures to protect user information.
- Data Sharing and Consent: As data is increasingly shared across platforms and services, regulators may focus on strengthening consent mechanisms to give individuals more control over how their data is used and shared.
Predictions for Future Changes
Based on current trends, it is predicted that data privacy laws will continue to evolve in response to technological advancements and emerging privacy risks. Regulators are likely to place greater emphasis on accountability, transparency, and individual rights to ensure that data is processed responsibly and ethically.
- Global Harmonization: There may be efforts to harmonize data privacy laws across different jurisdictions to create a more uniform regulatory framework and facilitate cross-border data transfers.
- Enhanced Enforcement Mechanisms: Regulators may introduce stricter enforcement measures, including higher fines and sanctions, to deter non-compliance with data privacy regulations and protect individuals’ rights.
- Focused Regulation on Specific Sectors: Some industries, such as healthcare and finance, may face sector-specific data privacy regulations tailored to address unique risks and challenges associated with their data processing activities.
Privacy by Design
Privacy by design is a concept in data privacy laws that emphasizes the integration of privacy and data protection measures into the design and development of products, services, and systems from the outset. By embedding privacy considerations into the design process, organizations can proactively address privacy risks and enhance data protection for individuals.
Incorporating Privacy by Design
- Implementing privacy by design principles involves considering privacy implications at every stage of product or service development.
- Organizations can conduct privacy impact assessments to identify and mitigate privacy risks early on.
- Anonymizing or pseudonymizing data to reduce privacy concerns and limit exposure of personal information.
- Offering privacy-enhancing features such as opt-in/opt-out mechanisms, data minimization, and encryption.
Benefits of Adopting Privacy by Design
- Enhanced data protection: By integrating privacy measures into the design process, organizations can better safeguard sensitive information and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Compliance with regulations: Adhering to privacy by design principles helps organizations comply with data privacy laws and regulations, avoiding potential fines and penalties.
- Building trust: Prioritizing privacy in product and service design can enhance customer trust and loyalty, leading to increased brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
- Cost-efficiency: Addressing privacy concerns early in the design phase can result in cost savings by avoiding retroactive changes and potential legal issues.
Data Privacy vs. Data Security
Data privacy and data security are two distinct but interrelated concepts that are crucial in the protection of sensitive information. Data privacy focuses on the proper handling of personal data, ensuring that individuals have control over how their information is collected, used, and shared.
On the other hand, data security involves safeguarding data from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats.
Addressing Data Privacy and Data Security Concerns
Data privacy laws play a critical role in addressing both data privacy and data security concerns. These regulations establish guidelines and requirements for organizations to protect personal data from unauthorized access and ensure that individuals’ privacy rights are respected. By implementing measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, companies can enhance both data privacy and security.
Interplay between Data Privacy Regulations and Cybersecurity Measures
The interplay between data privacy regulations and cybersecurity measures is essential for comprehensive data protection. Data privacy laws set the framework for how organizations should handle personal data, while cybersecurity measures provide the technical tools and protocols to secure this information.
Together, these efforts create a layered approach to safeguarding data, minimizing the risk of breaches and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
Enforcement Mechanisms
Data privacy laws are only effective if they are enforced properly. Enforcement mechanisms are essential to ensure that organizations comply with these regulations and protect the personal data of individuals. Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in monitoring and enforcing data privacy laws, holding organizations accountable for any violations.
Let’s delve into the various enforcement mechanisms used and discuss some examples of significant enforcement actions taken against organizations.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies, such as the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) in the UK or the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the US, are responsible for overseeing compliance with data privacy laws. These bodies have the authority to investigate complaints, conduct audits, and impose fines on organizations that fail to protect the personal data of individuals.
They play a critical role in ensuring that organizations uphold the principles of data privacy and take appropriate measures to safeguard sensitive information.
Examples of Enforcement Actions
- In 2019, the FTC fined Facebook $5 billion for violating consumer privacy by mishandling user data and failing to protect it from third-party app developers.
- The ICO imposed a fine of £20 million on British Airways for a data breach that exposed the personal and financial information of more than 400,000 customers.
- Google was fined €50 million by the French data protection authority, CNIL, for lack of transparency, inadequate information, and lack of valid consent regarding personalized ads.
These examples illustrate the significant consequences that organizations face when they fail to comply with data privacy laws. Enforcement actions serve as a deterrent and emphasize the importance of prioritizing data protection to maintain consumer trust and avoid hefty penalties.
Conclusive Thoughts
As we reach the end of this rollercoaster ride through Data Privacy Laws, remember to keep your passwords secure and your privacy settings intact. Stay safe out there in the digital jungle, folks!

