Healthcare Compliance sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with Leila S. Chudori’s author style and brimming with originality from the outset.
As we delve deeper into the realm of Healthcare Compliance, a world of regulations, ethics, and patient safety unfolds before us, shaping the foundation of quality care in the medical field.
Importance of Healthcare Compliance
Healthcare compliance is a critical aspect of the medical field that ensures healthcare providers adhere to laws, regulations, and ethical standards to protect patient safety, privacy, and quality of care.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with healthcare regulations can result in severe consequences for healthcare organizations and professionals. Some examples include:
- Financial penalties and fines
- Loss of reputation and trust
- Litigation and legal action
- Exclusion from participation in government healthcare programs
Ensuring Patient Safety and Quality Care
Healthcare compliance plays a crucial role in safeguarding patient safety and ensuring quality care by:
- Implementing proper protocols and procedures
- Protecting patient data and privacy
- Promoting transparency and accountability
- Preventing medical errors and malpractice
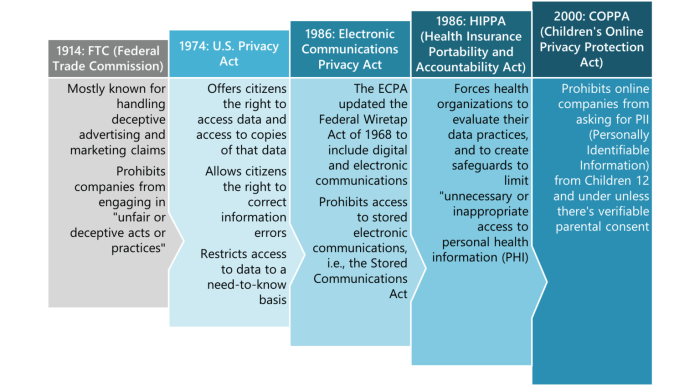
Key Regulations in Healthcare Compliance
Healthcare providers are subject to a multitude of regulations to ensure patient safety, data security, and overall compliance with industry standards. Let’s delve into some of the key regulations that healthcare organizations must adhere to.
Major Regulatory Bodies
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): Responsible for overseeing federal healthcare programs and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Regulates the safety and effectiveness of medical devices and pharmaceuticals.
- The Office for Civil Rights (OCR): Enforces HIPAA regulations related to patient privacy and data security.
Specific Laws and Regulations
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA sets standards for the protection of sensitive patient health information, including electronic medical records. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal penalties.
- The Affordable Care Act (ACA): Also known as Obamacare, this law aims to improve access to healthcare and regulate insurance practices.
- The Anti-Kickback Statute: Prohibits healthcare providers from offering or receiving incentives in exchange for patient referrals.
Implications of HIPAA
-
HIPAA compliance is crucial for safeguarding patient confidentiality and preventing unauthorized access to sensitive health information.
- Healthcare organizations must implement stringent security measures, such as encryption and access controls, to protect patient data from breaches.
- Failure to comply with HIPAA regulations can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Implementing Compliance Programs
Developing a healthcare compliance program is crucial for ensuring that healthcare organizations adhere to regulations and ethical standards. Here are the steps involved in creating an effective compliance program:
Step 1: Conducting a Risk Assessment
A thorough risk assessment helps identify areas of potential non-compliance within the organization. This involves evaluating current processes, policies, and practices to pinpoint areas that require improvement.
Step 2: Establishing Policies and Procedures
Once risks are identified, the organization must develop comprehensive policies and procedures to address these risks. These policies should Artikel the expected behaviors and actions to ensure compliance with regulations.
Step 3: Training and Education
Training and education play a vital role in ensuring that healthcare staff understand their compliance responsibilities. Regular training sessions should be conducted to keep employees informed about regulatory changes and best practices.
Step 4: Monitoring and Auditing
Regular monitoring and auditing of compliance activities are essential to detect any potential issues or non-compliance. This step helps in assessing the effectiveness of the compliance program and making necessary adjustments.
Step 5: Reporting and Investigation
Establishing a system for reporting compliance concerns and conducting investigations is crucial for addressing any violations promptly. This promotes transparency and accountability within the organization.
The Role of Technology
Technology plays a significant role in monitoring and enforcing compliance within healthcare organizations. Utilizing compliance management software can help automate processes, track compliance activities, and generate reports for analysis.
Training and Education in Compliance
Training and educating healthcare staff on compliance policies and procedures are essential for ensuring adherence to regulations. This includes providing regular training sessions, workshops, and resources to keep employees updated on compliance requirements.
Monitoring and Enforcement with Technology
Technology can aid in monitoring and enforcing compliance by providing tools for tracking compliance activities, conducting audits, and generating reports. This allows organizations to identify any potential issues and take corrective actions promptly.
Data Security and Privacy
Data security is a critical aspect of healthcare compliance, especially when it comes to safeguarding patient information and ensuring privacy regulations are met. In today’s digital age, where data breaches are increasingly common, healthcare organizations must prioritize the security of sensitive information to maintain trust with patients and comply with relevant laws.
Methods for Safeguarding Patient Data
- Implementing access controls: Limiting access to patient data to only authorized personnel can help prevent unauthorized disclosure.
- Regular staff training: Educating employees on data security best practices and the importance of patient confidentiality can help mitigate risks.
- Utilizing encryption: Encrypting patient data both at rest and in transit can add an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Secure communication channels: Using secure communication methods such as encrypted email or secure messaging platforms can help ensure that patient information is transmitted safely.
Role of Encryption and Secure Communication
Encryption plays a crucial role in maintaining data security by converting sensitive information into a code that can only be deciphered with the correct key. Secure communication methods, such as encrypted emails or messaging platforms, help prevent unauthorized access to patient data during transmission.
By utilizing encryption and secure communication channels, healthcare organizations can enhance data security and privacy compliance, ultimately protecting patient information from potential threats.
Auditing and Monitoring Compliance
Auditing and monitoring compliance in healthcare is a crucial aspect of ensuring that organizations adhere to regulations and guidelines set forth to protect patient information and maintain quality care. By conducting regular audits and monitoring processes, healthcare facilities can identify areas of non-compliance and take corrective actions promptly.
Process of Conducting Audits
Auditing in healthcare compliance involves reviewing policies, procedures, and practices to ensure they align with regulatory requirements. This process includes examining documentation, conducting interviews, and analyzing data to assess the effectiveness of compliance programs.
Key Metrics and Indicators
- Number of compliance violations identified
- Rate of compliance training completion
- Percentage of staff following proper procedures
- Timeliness of reporting incidents
- Audit findings resolution time
Significance of Monitoring and Auditing
Regular monitoring and auditing are essential to maintaining compliance standards in healthcare. It helps organizations detect issues early, prevent potential risks, and improve overall compliance efforts. By continuously evaluating and adjusting compliance programs, healthcare facilities can mitigate legal and financial risks while ensuring the safety and well-being of patients.
Handling Non-Compliance Issues
When non-compliance issues are identified in healthcare, it is crucial to have a structured approach to address them effectively. This involves understanding the steps to be taken, the consequences for individuals or organizations found to be non-compliant, and the development of corrective action plans.
Identifying Non-Compliance
Non-compliance issues can be identified through various means such as internal audits, whistleblower complaints, or regulatory inspections. Once identified, it is essential to thoroughly investigate the root cause of the non-compliance to prevent recurrence.
- Conduct a comprehensive review of the non-compliant behavior or practice.
- Identify the individuals or departments involved in the non-compliance.
- Document all findings and evidence related to the non-compliance issue.
Effective communication and collaboration among all stakeholders are key to addressing non-compliance issues promptly and effectively.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance in healthcare can have serious consequences for both individuals and organizations. These consequences may include financial penalties, legal actions, reputational damage, and even exclusion from participation in government healthcare programs.
- Individuals may face disciplinary actions, termination of employment, or loss of professional licenses.
- Organizations may incur hefty fines, face lawsuits, or experience a decline in patient trust and satisfaction.
Developing Corrective Action Plans
To address non-compliance effectively, healthcare organizations must develop corrective action plans that Artikel specific steps to rectify the issues and prevent their recurrence in the future.
- Establish clear goals and objectives for the corrective action plan.
- Assign responsibilities to individuals or teams for implementing the plan.
- Set deadlines for each action item and monitor progress regularly.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of the corrective actions taken and make necessary adjustments if needed.
Ethical Considerations in Healthcare Compliance

Maintaining healthcare compliance involves navigating various ethical dilemmas that healthcare professionals may encounter. Ethical decision-making plays a crucial role in ensuring that compliance-related issues are addressed in a responsible and morally sound manner.
Ethical Dilemmas in Healthcare Compliance
- One common ethical challenge is balancing patient confidentiality with the need to disclose information for compliance purposes.
- Healthcare professionals may face conflicts of interest when complying with regulations that could potentially impact their financial incentives.
- The pressure to meet regulatory requirements while providing quality patient care can lead to ethical dilemmas regarding resource allocation.
Importance of Ethical Decision-Making
- Ethical decision-making ensures that healthcare compliance is not just a matter of following rules, but also upholding the values of integrity and transparency.
- By prioritizing ethical considerations, healthcare professionals can build trust with patients, colleagues, and regulatory bodies.
- Ethical decision-making fosters a culture of accountability and responsibility within healthcare organizations.
Examples of Ethical Challenges
- A healthcare provider may face ethical dilemmas when deciding whether to report a colleague who is not adhering to compliance regulations.
- Conflicts may arise when disclosing potential errors or violations that could harm the reputation of the healthcare institution.
- Balancing the need for cost-effective practices with patient safety and quality care poses ethical challenges in healthcare compliance.
International Perspectives on Healthcare Compliance
In today’s globalized world, healthcare compliance standards vary across different countries, presenting unique challenges for organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions. Ensuring global compliance in healthcare practices requires a deep understanding of the regulatory landscape in each country and the ability to navigate complex legal requirements.
Comparison of Healthcare Compliance Standards
- Healthcare compliance standards in the United States, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), focus on protecting patient data and ensuring privacy.
- In the European Union, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict guidelines for the collection, storage, and processing of personal data, including health information.
- Countries in Asia, like Japan and South Korea, have their own regulations governing healthcare compliance, emphasizing data security and patient confidentiality.
Challenges of Ensuring Global Compliance
- Language barriers and cultural differences can complicate compliance efforts, making it challenging to interpret and implement regulations effectively.
- Differing regulatory frameworks and enforcement mechanisms across countries require organizations to adapt their compliance programs to meet local requirements.
- Managing compliance in a global context necessitates continuous monitoring, training, and communication to ensure alignment with diverse regulatory expectations.
Impact of International Collaborations
- International collaborations and agreements, such as mutual recognition agreements and data-sharing protocols, can facilitate compliance by promoting harmonization of standards and practices.
- Participation in global healthcare initiatives and forums allows organizations to stay informed about emerging trends and best practices in compliance, enabling them to enhance their programs proactively.
- Cross-border partnerships and information exchanges enable stakeholders to address common challenges, share resources, and collectively advance healthcare compliance on a global scale.
Continuous Improvement in Compliance Programs
Continuous improvement in healthcare compliance refers to the ongoing process of evaluating and enhancing compliance programs to ensure they remain effective and up to date. This proactive approach helps organizations adapt to changes in regulations, technology, and best practices, reducing the risk of non-compliance and potential legal issues.
Strategies for Evaluating and Enhancing Compliance Programs
- Regular Assessments: Conduct regular assessments of compliance programs to identify areas for improvement and address any gaps or weaknesses.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establish feedback mechanisms to gather input from stakeholders, including employees, patients, and regulators, to identify potential issues and opportunities for improvement.
- Continuous Training: Provide ongoing training and education to employees to ensure they are aware of the latest compliance requirements and best practices.
- Technology Integration: Leverage technology solutions, such as compliance management software, to streamline processes, monitor compliance activities, and generate real-time reports for analysis.
Best Practices for Maintaining a Culture of Continuous Improvement
- Leadership Support: Ensure that senior management is actively involved in promoting a culture of compliance and continuous improvement throughout the organization.
- Transparency and Accountability: Foster a culture of transparency and accountability where employees feel comfortable reporting compliance issues and are held responsible for their actions.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential compliance risks and prioritize areas for improvement based on the level of risk exposure.
- Performance Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to measure the effectiveness of compliance programs and track progress over time.
Emerging Trends in Healthcare Compliance
The landscape of healthcare compliance is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing regulations. In this section, we will explore some of the emerging trends shaping the future of healthcare compliance practices.
Impact of Telemedicine and Digital Health
Telemedicine and digital health technologies have revolutionized the way healthcare services are delivered, providing patients with convenient access to care from remote locations. However, these innovations also pose new challenges for compliance regulations. Healthcare organizations must ensure that patient data is securely transmitted and stored in compliance with privacy laws such as HIPAA.
Telemedicine platforms need to adhere to strict regulations to protect patient information and maintain the quality of care provided.
Artificial Intelligence in Compliance Processes
Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly being utilized to streamline compliance processes in healthcare. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential risks more efficiently than manual methods. By automating routine compliance tasks, AI can enable healthcare organizations to stay ahead of regulatory changes and proactively address compliance issues.
However, the use of AI in compliance also raises ethical considerations regarding data privacy, bias, and transparency. Organizations must ensure that AI algorithms are fair, transparent, and compliant with regulatory requirements to maintain trust and integrity in their compliance practices.
Legal and Ethical Challenges in Healthcare Compliance
In the realm of healthcare compliance, navigating the complex landscape of legal and ethical considerations is essential to ensure the delivery of quality care while maintaining integrity and adherence to regulations.
Intersection of Legal and Ethical Considerations
Legal requirements and ethical principles often intersect in healthcare compliance, posing challenges for organizations striving to meet both sets of standards simultaneously. While laws provide a framework for compliance, ethical considerations guide decision-making in morally ambiguous situations.
Conflicting Laws and Ethical Principles
Conflicting laws and ethical principles can create dilemmas for healthcare organizations, as they may be required to comply with regulations that conflict with their ethical values. For example, a law mandating data sharing for public health purposes may conflict with patient privacy rights, leading to ethical dilemmas.
Strategies for Navigating Legal and Ethical Challenges
- Establish clear policies and procedures that align with both legal requirements and ethical principles.
- Provide ongoing training to staff on the importance of ethical decision-making and compliance with laws.
- Consult legal and ethical experts when faced with challenging situations to ensure the best course of action is taken.
- Regularly review and update compliance programs to address emerging legal and ethical issues in healthcare.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, Healthcare Compliance serves as the cornerstone of a system designed to protect patients, uphold standards, and ensure ethical practices within healthcare organizations. Through a blend of regulations, technology, and ethical considerations, the journey towards compliance continues to evolve, driving continuous improvement and embracing emerging trends in the ever-changing landscape of healthcare.